In the high-stakes game of data privacy, marketing agencies are finding themselves on the hook for liabilities that can run into the millions. Gone are the days when a handshake and good intentions were enough. Now, clients are demanding that agencies put their money where their mouth is. Some companies are only considering agencies willing to cough up $15 million if they fumble the data ball. It’s a litmus test to see whether agencies are taking data privacy as seriously as they claim.
Importance of Data Governance for Agencies
For agencies, this presents a dilemma. They must tread the fine line between securing business and handling the inherent risks associated with data, especially when third parties are in the mix.
So, what’s an agency to do when clients are demanding liability commitments ranging from a “mere” $5 million to an eye-watering $100 million?
It’s made one thing abundantly clear: Agencies can no longer afford to play fast and loose with how they handle data.
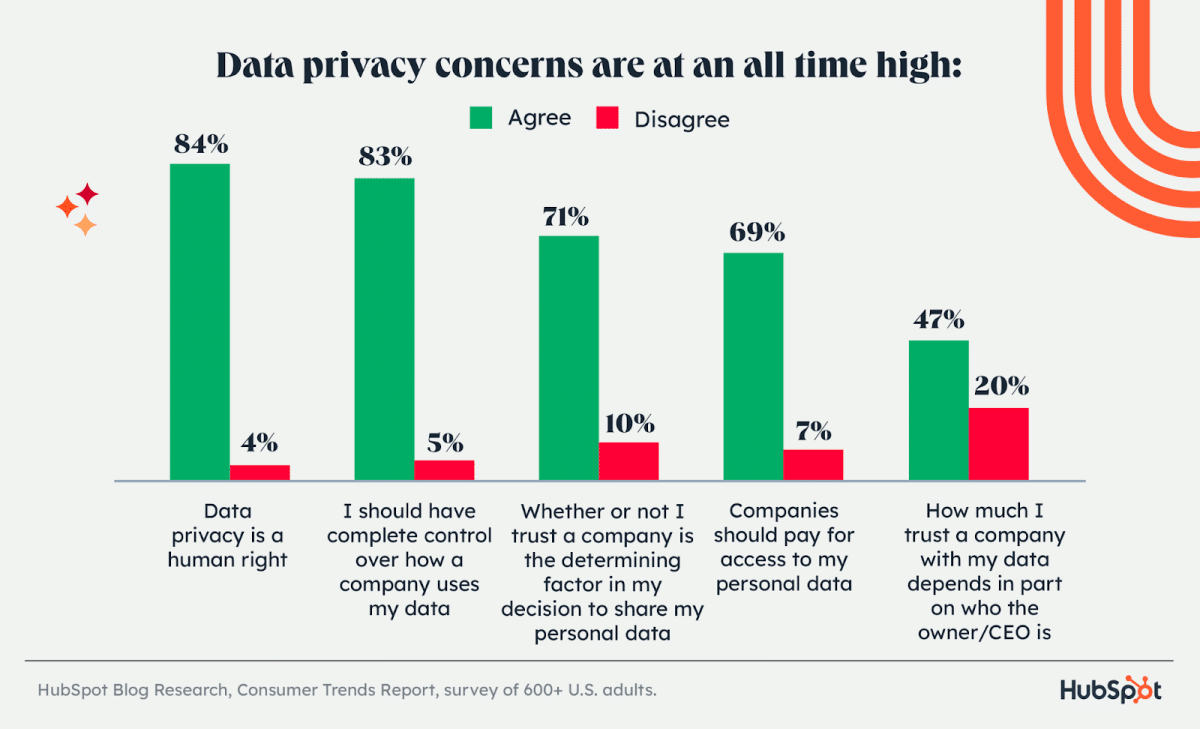
After all, data privacy concerns are at all all-time high, according to the latest Consumer Trends Report from HubSpot:
If you want to protect your agency from financial ruin and keep your clients’ trust, you’ve got to take data privacy and security seriously. And that starts with proper data governance.
What Is Data Governance?
Data governance is everything you do to ensure data is secure, private, accurate, available, and usable.
In the context of agencies, data governance is the structured approach to managing:
- Client data
- Campaign metrics
- Audience insights
- And more
Data governance means ensuring that every piece of data—be it a client’s proprietary information, audience demographics, or campaign results—is handled with the utmost precision and security.
So why should digital and marketing agencies care?
There are plenty of good reasons to care about data governance:
- You want clients to trust you enough to actually do business with you.
- You want to ensure that you are able to keep the trust given to you.
- You want to avoid the steep fines for non-compliance with GDPR.
- You want to make ethical decisions regarding how you use data.
- You want to ensure the data you have is accurate and accessible to the right people.
Because doing so will allow you to extract better insights, make better business decisions, and have a better ROI for your clients.
Those all sound like pretty compelling reasons if you ask me.

Source: Midjourney. Prompt: An image depicting data governance
Get Started With Data Governance
Now, your agency needs to think about a few items before it jumps into data governance. (Data governance is definitely one of those “look-before-you-leap” types of situations.)
Ask the following questions.
1. What are your primary goals for a data governance framework?
Is it risk mitigation, data quality improvement, regulatory compliance, or something else? Understanding your key drivers, whether regulatory, operational, or strategic, can help frame the governance approach.
2. Do you, or does someone on your team, have the right expertise?
It’s important to recognize if you are out of your league here. If you aren’t sure exactly, here’s a one question quiz to find out where you are at:What’s the difference between data privacy and data security?
(long pause)
Did you have to look up the definitions? Or perhaps you thought they meant the same thing?
The answer is:
Data privacy is about ensuring proper and ethical use of personal data by giving individuals control over how their data is accessed, used, or shared. On the other hand, data security is the methods and mechanisms used to keep that data safe from unauthorized access or external threats.
If you didn’t know that, you should with someone who does know the difference between the two terms (ideally, sans Googling the answer). Consider working with a company who specializes in data governance (Yes, data-governance-as-a-service, or DGaaS, is a real thing.)
David Godlewski, CEO of Intelliverse, says that his company hired data analysts dedicated to data management to help keep sensitive data secure.
“Our process began with a meticulous assessment of data vulnerabilities and requirements,” says Godlewski. “After recognizing the need for expertise in this critical area, we hired data analysts with specialized backgrounds in cybersecurity, data governance, and compliance.
“These analysts now play a pivotal role in crafting, implementing, and monitoring our data management policies.”
Alternatively, you can get the training necessary for your team to get up to speed. But either way, you need to make sure you’ve got the right people in place to help guide your agency through the process, because creating a data governance framework can be a bit cumbersome to say the least.
Establish a Data Governance Framework for Agencies
There is one more preliminary step that is necessary before you start creating your data governance framework, and that is to conduct a data audit.
Conduct a data audit
By conducting a data audit, you will be able to gain a better understanding of your data infrastructure as it currently exists. That way, you know exactly where things are at right now, which makes figuring out the next steps a lot easier.
This auditing process involves taking a meticulous inventory of all data assets within your agency. Begin by identifying every data source, be it from client records, marketing insights, transactional data, or other digital assets. Also identify where this data is housed—whether in cloud storage, on-premise servers, or external databases.
Once you have identified all of your data sources, evaluate the sensitivity of the data. Different types of data have varying levels of sensitivity and should be treated accordingly. For instance, personal client details would demand a higher level of protection than general market statistics.
Arham Khan is the co-founder of UK-based marketing agency Pixated. Within his agency, data classification is an important first step of their data management process.
“We organize our data into categories based on its value to the company, then update these classifications as and when data is created, altered, processed, or transmitted,” says Khan.
“We’ve also innovated several policies to guarantee that these classifications can’t be falsified, and ensure that only privileged members of the team can access the data to up- or downgrade the classification of any given set.”
Understanding and classifying your data in this way will help prepare the groundwork for the subsequent steps in the governance framework, particularly concerning data protection and access controls.
Develop data governance policies and procedures
The backbone of an effective data governance framework is the set of policies and procedures that guide how data is managed, accessed, and protected. Here are the most essential policies that should be included as part of your data governance strategy:
1. Data access policy
First and foremost, establish clear access control guidelines. Dictate who within the agency can access specific data sets, underlining the importance of role-based access. This ensures that only those with the necessary permissions can view or manipulate sensitive data. Incorporating tools like multi-factor authentication can further fortify these controls.
2. Data quality policy
You will need to define standards for data accuracy, completeness, reliability, and timeliness. This should also include procedures for things like data validation, cleansing and correction.
3. Data privacy policy
Consumers today are more aware of their digital rights, and an oversight in data privacy could be the difference between maintaining loyal customers and losing trust. Not only that, the regulatory bodies that govern data privacy are handing out huge fines for the companies that aren’t up to snuff. You cdon’t want to be like X (formerly TikTok), which earlier this year was handed a jaw-dropping fine of $345 million euros for not complying with GDPR.
So, that being said, here’s what you need to consider when creating your data privacy policy:
- Aim for clear and concise writing. No need to get fancy with a bunch of confusing legalese. Just write the policy in plain and simple terms that make it easy to understand.
- Make sure that you are upfront by including:
– The type of data you collect (personal, demographic, behavioral)
– Why you are collecting the data (marketing, improving user experience, third-party sharing)
– How you collect the data (cookies, forms, third-party tools)
– How the data is stored
– Who has access to the dataIt is also important to inform users how long you intend to keep their data and the criteria used to determine this duration. Additionally, If you’re sharing data with third parties, list them. Also, explain the purpose behind this sharing, and ensure these third parties maintain the same level of data protection. - If you operate globally, acknowledge different jurisdictions and their specific requirements such as GDPR for Europe, CCPA for California, etc. Ensure your data privacy policy is compliant across all regions you operate in.
- Finally, you should highlight the rights users have regarding their data. This includes access, correction, deletion, and the right to object to processing. Ensure there’s a straightforward process for users to exercise these rights. Provide clear channels for users to reach out with questions, concerns, or requests related to their data.
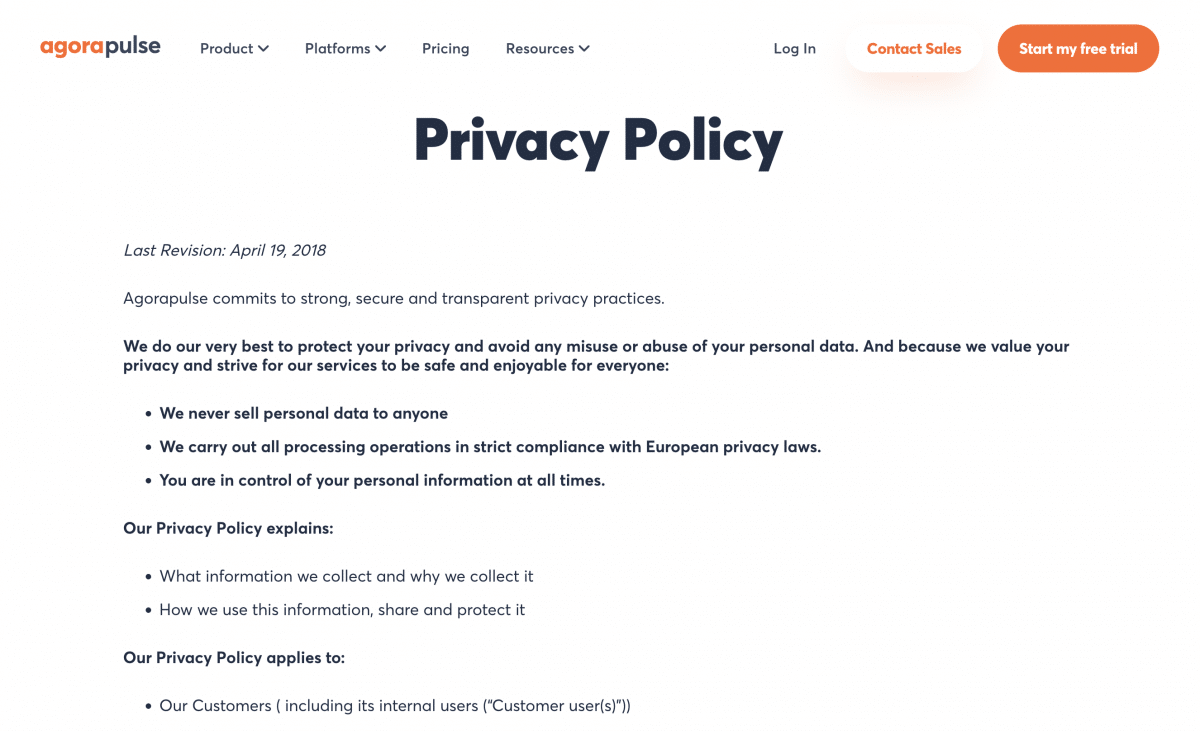
Agorapulse’s privacy policy clearly outlines what information is collected and how and why we collect it.
“Don’t just collect customer data for the sake of it,” says Draven McConville, CEO of Klipboard. “Only collect the data you need for specific purposes, such as sending them targeted marketing messages or providing them with better customer service. Be transparent about how you are using the data, and give your customers a chance to opt out of the data collection.”
Ultimately, the point of your privacy policy is to build trust with clients and consumers, so keep that in mind when writing, and you’ll be on the right track.
4. Data retention and deletion policy
An often-overlooked aspect of data governance is the policy concerning data retention and deletion. It’s not enough to collect and store data – you must also determine how long it’s relevant and when it should be purged. Establish clear timelines, especially for sensitive data, to ensure that it’s securely deleted once it’s no longer needed.
Note: Be aware that some types of data may have legally mandated retention periods in your jurisdiction, so be sure to take that into account when creating your policy.
5. Data protection policy
Protecting data at all points—whether in transit or at rest—is paramount. Employing strong encryption algorithms ensures that even if data falls into the wrong hands, it remains unintelligible and, therefore, useless.
Here’s some additional items you may want to include your data protection policy:
- Data at rest:
Ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. Implement role-based access control systems to limit access based on job function.
Use advanced encryption techniques to protect stored data. Consider solutions like Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for databases.
Schedule routine backups of data and ensure these backups are encrypted and stored securely, preferably in multiple locations. - Data in transit:
Use secure transmission protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) to ensure data is encrypted while being transmitted over networks.
Encourage the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) when accessing company data from unsecured networks, like public Wi-Fi.
For non-essential transfers or for users who don’t require full data, use data-masking or anonymize sensitive information where possible. - Physical security:
If maintaining physical servers, ensure they’re in a secure location with limited access. This includes biometric locks, surveillance, and intrusion alarms.
Ensure laptops, hard drives, and other portable storage devices are encrypted and have secure passwords.
Your agency will likely have many other things to include within your data protection policy. The above list will give you a start on the basics.
6. Data breach policy
Although the goal is to prevent data breaches, it’s essential to have a detailed plan in case one occurs. Your response plan should contain steps for containment, assessment, notification, and recovery.
- Immediate containment: The first moments after detecting a breach are crucial. Define immediate actions to contain the breach, such as isolating compromised systems or temporarily shutting down certain access points.
- After immediate threats are managed, you should then look to prevent further unauthorized access. This could involve changing passwords, patching vulnerabilities, or updating firewalls.
- Assessment: Identify what data was accessed, how it was accessed, and the duration of the breach. Tools like system logs can be crucial here, or you may consider partnering with a cybersecurity firm for looking into data forensics.
- Notification: Determine when and how to notify affected parties. This includes internal stakeholders, clients, and, if necessary, the general public. Craft clear, transparent, and reassuring messages ahead of time to avoid miscommunication during a crisis.
- You also need to understand the reporting obligations under regulations like GDPR or CCPA. Ensure procedures are in place for timely reporting to authorities when required.
- Recovery: After handling the immediate crisis, review the incident in-depth. Understand its root cause, learn from any missteps, and adjust your response plan accordingly so it doesn’t happen again.
By creating your data breach policy and procedures, you can be prepared in advance with proactive steps for minimizing damage, and a plan to restore trust should a breach occur.
Training and Education
In the agency context, every campaign, every strategy, hinges on collaboration. The same holds for data governance. It’s imperative that everyone—from the account manager to the creative director—understands and values the role of data governance. Their collective endorsement is key to a successful shift towards a data-conscious culture within your agency.
Source: Created using Midjourney using the prompt below.
A hand shaking another hand with a digital overlay, signifying collaboration in data governance.
Start by introducing a comprehensive onboarding program for new employees. Ensure they are made aware of your agency’s data governance policies from day one. This foundational understanding sets the tone for the level of seriousness and commitment expected concerning data handling.
But onboarding is just the beginning. Regular training sessions should be scheduled throughout the year. These sessions should not only cover the basic principles, but also cover the nuances of data governance, particularly data security and privacy.
Tristan Harris, demand generation manager at Thrive Marketing Agency, says building a robust internal training program has helped his agency implement an effective data governance strategy.
“We’ve trained every team member on data management practices, creating a holistic understanding of this critical aspect across our agency rather than confining it to a select group of data analysts,” says Harris.
“The training extends beyond basic data handling to include concepts of data privacy, data security, and the ethical use of data. This rigorous process ensures optimal data security and privacy management.”
Creating an in-depth training program for agency employees can also help them understand the importance of their role in the larger security framework, and encourage a security-conscious culture. That way, employees will feel empowered to voice concerns and help stay vigilant against potential threats.
By making data security a collective responsibility, your agency will not only strengthen its defense against breaches but also create a sense of ownership and ultimately, a more effective data governance program.
Vendor management
It’s likely that your agency relies on third-party vendors for various services, which means the chain of data governance extends beyond your agency’s walls. When partnering with new vendors, it is important to thoroughly understand their data management and security practices before entering any contractual agreement.
Take the time to assess their data security policies. Do they align with yours? Are they robust enough to ensure that the data you might share with them will be protected to the same standards you uphold?
You will want to also look at your legal agreements with each vendor. Ensure that every contract with a vendor has clearly defined data protection clauses. These clauses should articulate the responsibilities of the vendor in terms of data handling, storage, and protection. They should also define the ramifications in case of breaches or non-compliance.
A good example of this is the Google Cloud Trust Centre. It has everything you need to know laid out in a simple and easy to access format, and has the answers to any questions or concerns that you may have regarding their data security and privacy practices.
Being transparent and upfront in this manner helps to establish trust and will ultimately make it easier to work with other vendors.
Additionally, always have a plan for data transition. In scenarios where a vendor relationship ends, or a service is transitioned to another party, there should be clear procedures for how data is transferred, stored, or deleted, ensuring that no gaps arise in the data governance chain during the transition.
Monitor, review and adjust
The establishment of a data governance framework is not a one-time event but a living process that requires ongoing attention. This means that you should have regular audits to help identify gaps or inefficiencies in your data governance framework.
Equally important is the feedback loop; Every team member, from top-level executives to entry-level employees, should have channels available to report potential risks, provide insights, or suggest improvements.
It’s especially crucial to review your data governance strategy in light of new laws, industry best practices, and technological advancements. This will likely lead to occasional adjustments in your approach, but will ultimately ensure your framework is compliant and effective.
Make Data Governance a Top Priority
Data is a valuable asset, and its protection should be a top priority for agencies looking to stay in tune with what consumers and clients expect from the companies they interact with. By establishing a comprehensive data governance framework, not only do agencies safeguard their reputation and follow regulatory compliance, they also ensure more efficient and informed decision-making. And the time invested in setting up this structure will be well worth the peace of mind and trust it will build with your clients.
Want a social media management tool that you can count on to keep your data secure? Agorapulse uses multiple security methods, including encryption with TLS, two-factor authentication, and intrusion detection solutions, to ensure that our customers’ data is safe at all times.
Check out the full list of security protocols we use, or, better yet, book a demo with a member of our team so they can answer any questions you may have.